Contents
1. GSAT-15 set to replace dying INSAT-3A and 4B
a) Utility of GSAT-15
b) Leased transponders
c) Other details
d) Previous GSAT Launch: GSAT-16
e) Why GSAT 16 was not launched by Indian Launch Vehicle?
2. Ariane 5 Launch Vehicle
a) Guiana Space Centre
3. Why are satellites launched from east coast in eastward direction and from locations that are close to equator?
a) Where is the best place to launch a rocket from?
b) Why at equator?
c) Why in eastward direction?
d) What about polar satellites (remote sensing and earth observation satellites)?
e) Why launch sites on east coast?
4. Why is Sriharikota a place suitable for launching rockets?
Other terms in satellite communication like, LEO, GTO, Geosynchronous orbit, Geostationary orbit, Transponders, PSLV, GSLV, Cryogenic Engine, Vikas engine, K band, S band, Ku band etc. will be explained in the next post
|
GSAT-15 set to replace dying INSAT-3A and 4B
· GSAT-15, the mainly communications satellite will be put in space in November, 2015.
· It will replace two ageing spacecrafts, INSAT-3A and INSAT-4B.
· INSAT-3A, launched in April 2003, has completed its 12-year life.
· INSAT-4B, flown in March 2007, got reduced to half its functions in 2010 after one of its two power-generating solar panels developed a snag.
Utility of GSAT-15
· Its 24 transponders are solely in the Ku band.
· They will cater to DTH (direct-to-home) television.
· They will cater to thousands of VSAT operators who provide broadband services; and DSNG (digital satellite news gathering) for TV news channels (This is how news reporters are able to quickly transfer information to their control centers).
· GSAT-15 will not add new transponder capacity to the country; it will ‘ensure sustainability of service’ for the capacity-hungry DTH sector.
· It will also carry the third GAGAN satellite navigation transponder as a back-up for airlines and other users of augmented GPS-based systems.
Leased transponders
· Indian DTH broadcasters have been forced to lease 59 transponders on foreign satellites over the region; less than half of that capacity (26) is allotted for DTH on Indian communication satellite. (This makes DTH costly)
· The immediate focus is on bridging the Ku-band shortage.
· ISRO intends to reduce dependence on external transponders in about two years.
· The heavyweight 4,000-kg-class GSAT-11 due in a couple of years, would add a significant number of transponders for the national users.
Other details
· Weight of GSAT-15 ==> 3,164 kg
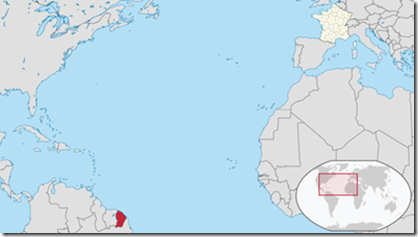
· It will be launched from Kourou in French Guiana (in South America) on the European Arianespace’s Ariane-5 launcher.
· The satellite cost and the launch fee ==> Rs. 860 crore.
· GSAT-15 will be flown along with Saudi Arabia’s Arabsat-6B/Badr-7.
· It will be stationed over the country at a slot at 93.5 degrees East longitude.
· The two Indian rockets -- PSLV and GSLV -- cannot pitch the weight of GSAT-15 to its slot 36,000 km high.
· ISRO had signed up Arianespace to launch GSAT-17, GSAT-18 and the heavier GSAT-11.
Previous GSAT Launch: GSAT-16
· Launched on December 7, 2014 by the Ariane-5 launch vehicle of Arianespace from Kourou, French Guiana.
· Ariane-5 precisely placed GSAT-16 into the intended Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
· ISRO`s Master Control Facility (MCF) at Hassan in Karnataka will start operating the satellite.
· The present orbit of the satellite will be raised to Geostationary Orbit of about 36,000 km altitude
GSAT-16
· 11th Indian communication satellite meant to increase the number of transponders that in turn enhance the satellite based telecommunication, television, VSAT services in India.
· Weight ==> 3,150 kg.
Why GSAT 16 was not launched by Indian Launch Vehicle?
· GSAT-16 is a 3-4 ton satellite and ISRO doesn’t have a Launch Vehicle that can carry a payload of more than 2 tons.
· PSLV can only launch satellites below 2 tons. GSLV can launch 3-4 ton payload only to Lower Earth Orbit.
· GSLV Mk III is capable of launching 4 ton satellite to Higher Earth Orbits. It is still in development stage.
Ariane 5 Launch Vehicle
· European rocket that is a part of the Ariane rocket family.
· It is an expendable launch system (The launch vehicle is not reusable).
· It is used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) and low Earth orbit (LEO).
· Ariane 5 rockets are manufactured under the authority of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES) [Space agency of France].
· Function è Heavy launch vehicle
· Launch sites è Guiana Space Centre
Guiana Space Centre
· French Guiana is an overseas department and region of France, on the north Atlantic coast of South America.
· The Guiana Space Centre or, more commonly, Centre spatial guyanais (CSG) is a French and European spaceport near Kourou in French Guiana.
Why are satellites launched from east coast in eastward direction and from locations that are close to equator?
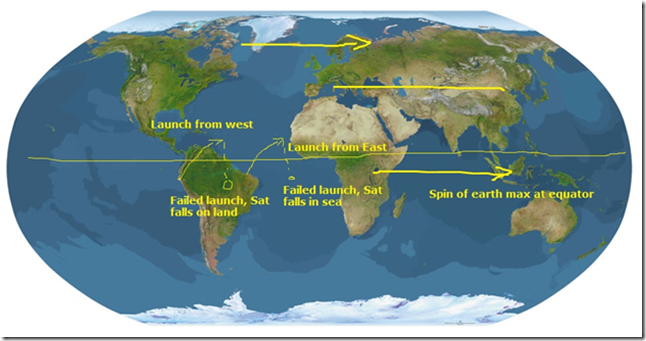
· If you observe the location of all the launch centers like Sriharikota, Kennedy Launch Center (USA: Florida), Guiana Space Centre etc., all are located on the East coast of the continent and are close to the equator.
Where is the best place to launch a rocket from?
· NASA has quite often had to “scrub” (cancel) launches from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida because of inclement weather.
· But why build a Space Centre in Florida in the first place? It’s location makes it particularly vulnerable to hurricanes and other weather “events”. (Compare this with Sriharikota).
· Florida is a good location for rocket launches because it is both on the east coast of the US and because it is close to the equator.
· In detail below.
Why at equator?
Reason 1
· Earth’s rotational velocity is maximum at the equator (on earth, centripetal force is maximum at the equator).
· When a spacecraft is launched into orbit, it should end up spinning around the Earth quickly enough not to be pulled back in by the Earth's gravity.
· The huge rockets used in launching a spaceship help this to happen by giving a huge amount of thrust, enough to achieve escape velocity.
· However, the spin of the Earth itself can help give it a push as well.
· Anything on the surface of the Earth at the equator is already moving at 1670 kilometers per hour (rotational velocity of earth).
Why in eastward direction?
· A satellite launched from the sites near the equator towards the east direction will get an initial boost equal to the velocity of Earth surface.
· This is similar to an athlete circling round and round before throwing a discus or a shot put.
[Escape Velocity is the minimum velocity needed for an object to escape earth’s gravitational pull. It is equal to 11.2 km/s or 40,270 km/h (25,020 mph).
In simple terms: If an abject is thrown towards the sky at a speed of 11.2 km/s or greater, it will have enough capacity to escape earth’s gravitational influence. If an object is thrown towards the sky at a speed lesser than 11.2 km/s, it will fall back to the earth after reaching a certain height.
Practically achieving this speed in the atmosphere is impossible as the object will burn up due to friction]
What about polar satellites (remote sensing and earth observation satellites)?
· But this benefit can be taken only for such satellites which are placed in geo-stationary orbit or which circle the Earth parallel to the equator.
· Such satellites are usually communication satellites or satellites used for scientific research such as ISS.
· There are other satellites which are placed in polar orbits moving across the equator in north south direction and used mainly for mapping or some times for spying.
· Such satellites are generally launched in south ward or north ward direction and therefore cannot take advantage of the Earth’s rotation.
Why launch sites on east coast?
· Another characteristic of launching satellites is that the launching stations are generally located near eastern coast line so that, just in case of failure of the launch, the satellite does not fall on built-up hinterland.
Reason 2
Communication satellites are put into geostationary orbit above the equator with zero inclination to the equatorial plane.
· The ideal place to launch to geostationary orbit is, obviously, on the equator.
· Equatorial launches only require the vehicle to bring the payload to orbital speed and do not require inclination changes.
· For launches that are not on the equator, the vehicle must perform a complex adjustment burn in the GTO (geostationary transfer orbit) phase of the mission to bring the vehicle an inclination of 0º.
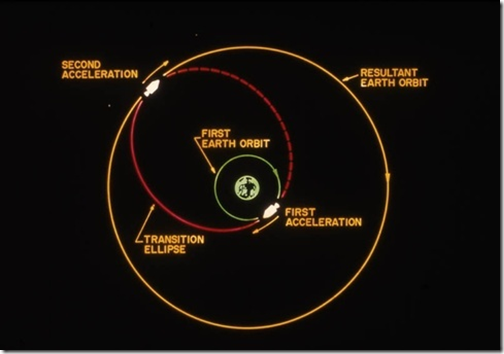
· The below image depicts this.
· The vehicle first reaches low earth orbit (green circle), then makes a burn to geostationary transfer orbit (the red ellipse), then makes a second burn to circularize the orbit into geostationary orbit (orange circle).
· When a vehicle is launched from the equator, the three orbits shown are planar (they lie in the same plane).
· If the vehicle is launched from a non-equatorial launch site, the green circle and the orange circle are non-planar, thus requiring the red ellipse to bridge the two orbits (More fuel will be required = high costs).
· This maneuver consumes propellant and thus decreases the payload. That's another reason why equatorial launches (or as close as possible) are preferred.
Why is Sriharikota a place suitable for launching rockets?
· All above points +
· It should be located away from populated areas.
· Since it involves moving of heavy equipment to the launch site, rail, road and/or shipping accessibility should be taken care of.
· Coastal areas become the preferred launch sites.
· Sriharikota fits all these requirements. Some of the other famous launch sites which fulfil these requirements in the world are: Kennedy site in Florida, U. S., Kourou in French Guiana, South America, San Marco in Africa and Alcantara in Brazil, South America.
0 comments:
Post a Comment